The Journey of a Diamond: From Mine to Market
Diamonds are one of nature’s most extraordinary creations. From their formation deep within the Earth’s mantle to their transformation into sparkling gemstones, every diamond has a fascinating story. This journey from mine to market reveals not just the natural origin of diamonds but also the craftsmanship, science, and global trade that turn them into symbols of love and luxury. In this blog, we will explore every stage in the journey of a natural diamond—mining, sorting, cutting, polishing, grading, and finally marketing them to the world.
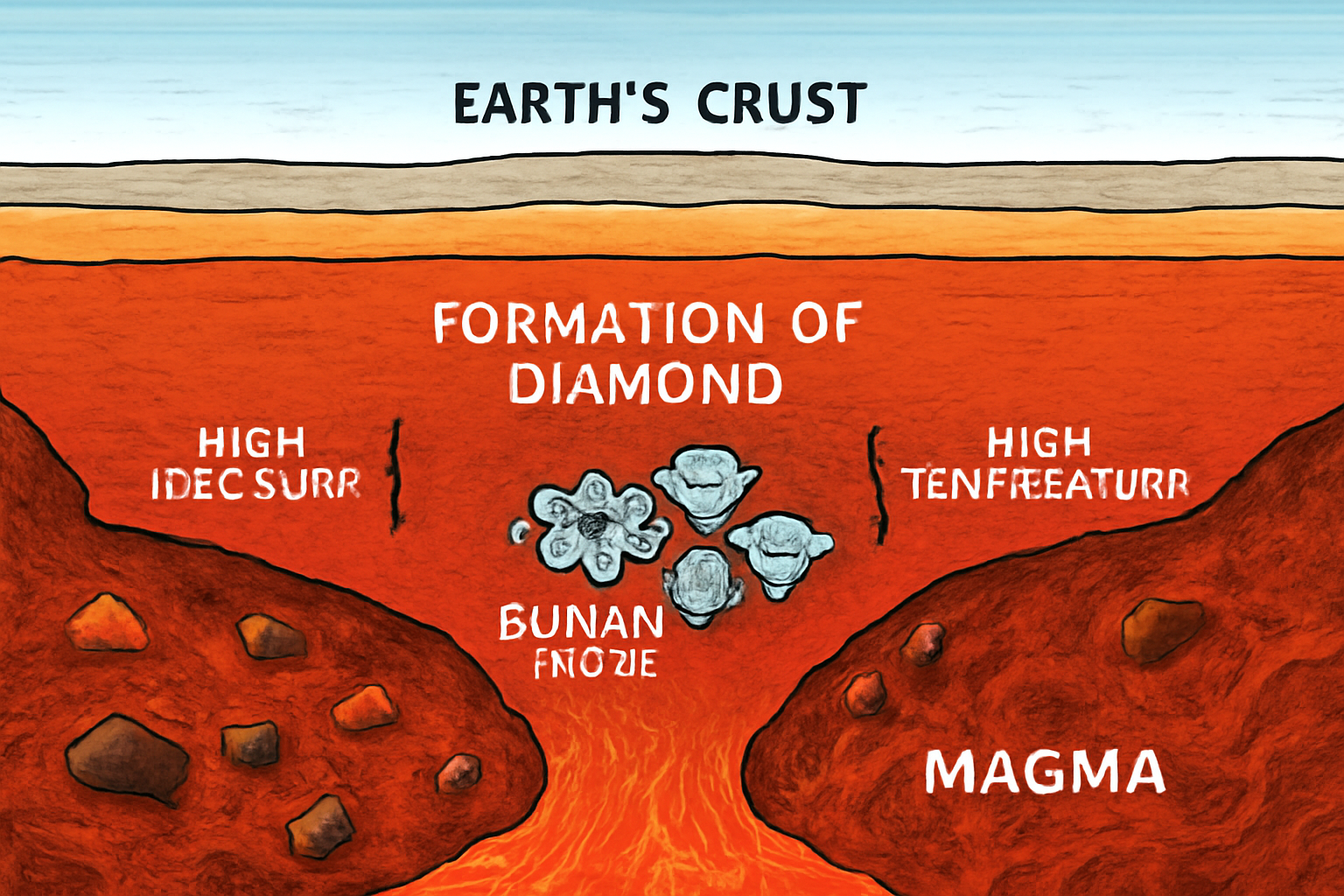
Formation of Diamonds in Nature
The journey of a diamond begins billions of years ago, nearly 150-200 kilometers below the Earth’s surface. Under extreme heat and pressure, carbon atoms bond in a unique crystalline structure, creating one of the hardest natural substances known to humankind. These crystals are carried to the Earth’s crust through volcanic eruptions, forming diamond-rich rocks known as kimberlites and lamproites.
The rarity of this geological process is what gives natural diamonds their exceptional value. Unlike synthetic diamonds, which can be made in laboratories, the natural growth process of diamonds over millions of years makes them a rare testament to Earth’s history.
Diamond Mining: Extracting Earth’s Treasures
Once diamonds are naturally formed, the next step in their journey is extraction through diamond mining. There are various mining methods depending on geography and deposits:
- Open-pit mining – Ideal for shallow deposits near the surface.
- Underground mining – Used for deposits located deeper in the Earth.
- Alluvial mining – Extracting diamonds from riverbeds and shorelines where they are carried by natural forces.
- Marine mining – Advanced techniques used to recover diamonds from the seabed.
Large mining companies primarily operate across Africa, Canada, Russia, and Australia. Ethical and sustainable mining practices are gaining importance, with initiatives ensuring that diamonds are conflict-free and mined with respect for the environment and communities.
Sorting and Rough Diamond Valuation
After extraction, rough diamonds are transported to sorting centers. Here, diamonds are categorized based on important attributes like size, shape, color, and clarity. Only about 20% of mined diamonds are gem-quality; the rest are used for industrial purposes.
Valuation of rough diamonds is a crucial stage. Experts estimate the yield and potential cuts to determine their market value. This is where the transformation of diamond mining results into polished gems begins.
The Art of Diamond Cutting and Polishing
One of the most fascinating parts of a diamond’s journey is its transformation from a rough stone into a sparkling gem. Skilled artisans, known as diamantaire, use advanced technology combined with centuries-old craftsmanship to cut and polish diamonds. The aim is to maximize brilliance and maintain weight while highlighting the diamond’s natural features.
The process involves several steps:
- Planning: Before cutting, diamonds are scanned with lasers to determine the best way to yield maximum value.
- Cleaving or Sawing: Rough stones are divided into smaller, workable pieces.
- Bruting: The diamond is shaped into a round outline or desired form.
- Polishing: Facets are carefully added to bring out the diamond’s brilliance.
- Final Inspection: Stones are analyzed under strict quality standards.
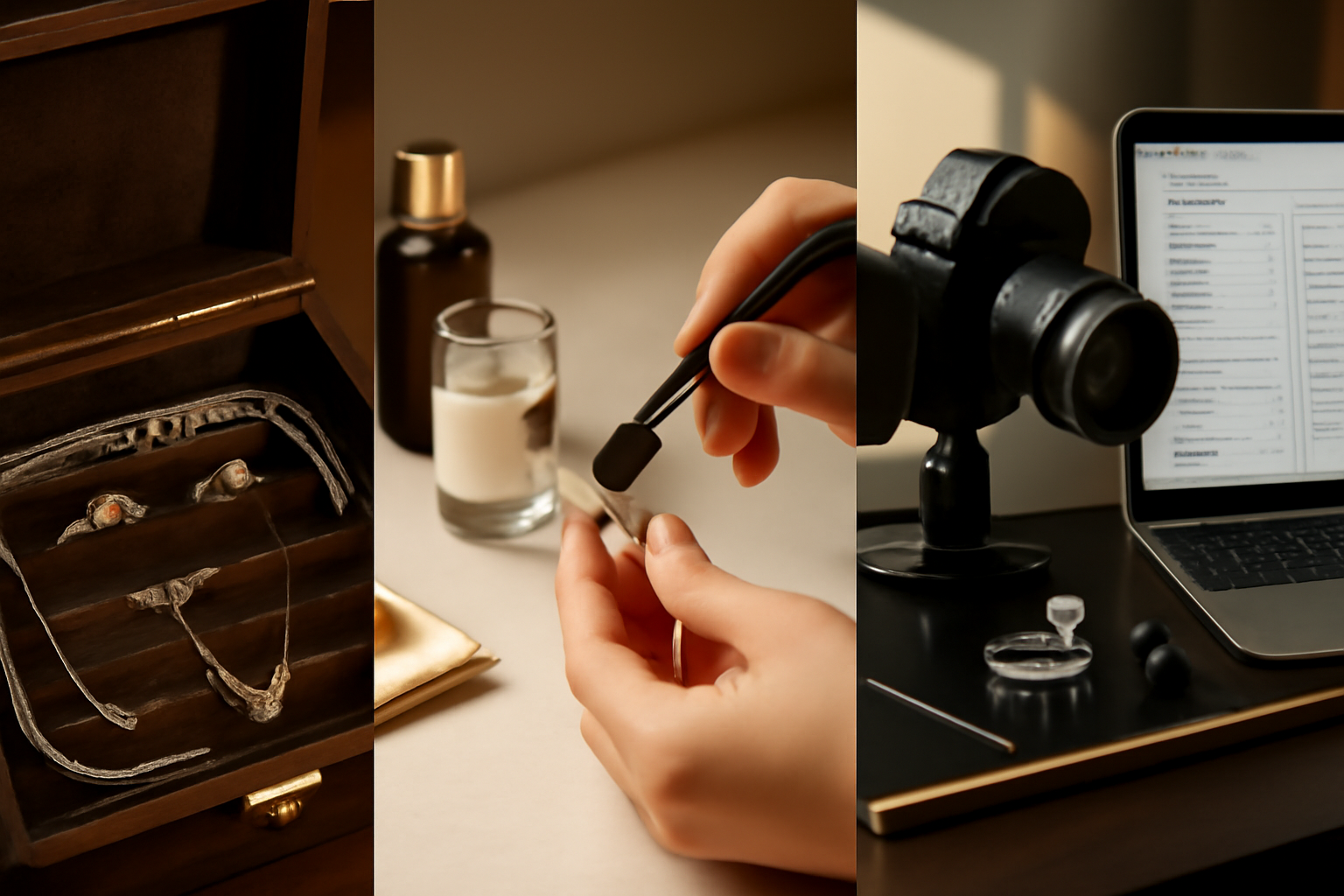
Diamond Grading and Certification
Grading is a scientific step where diamonds are evaluated according to the famous 4Cs: Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight. Reputable laboratories such as GIA (Gemological Institute of America), IGI, and HRD provide grading reports that verify authenticity and characteristics. A diamond certificate ensures transparency and trust for both jewelers and consumers.
This stage establishes the official identity of each polished diamond, ensuring that buyers can compare and purchase with confidence.
Global Diamond Market and Distribution
After certification, diamonds enter the global trade network. Major trading hubs such as Antwerp (Belgium), Dubai (UAE), Mumbai (India), and New York (USA) are key centers for diamond trading. Here, buyers and sellers negotiate deals and distribute stones across international markets.
India, particularly Surat, plays a dominant role in polishing and exporting diamonds. With skilled artisans and advanced infrastructure, nearly 90% of the world’s polished diamonds pass through India’s diamond industry.
From Jewelers to Consumers: The Final Step
The journey of a diamond completes when it reaches jewelers’ showcases and eventually finds a home with its owner. Whether set in an engagement ring, wedding band, pendant, or earrings, the brilliance of a diamond jewelry piece symbolizes love, commitment, and status.
Consumers are now more aware than ever about the origin of their diamonds. Ethical sourcing, sustainability, and certified authenticity play a vital role in purchasing decisions.
The Importance of Ethical and Sustainable Diamonds
Modern diamond buyers are not just interested in sparkle but also in the story behind the stone. Conflict-free certifications, responsible mining, and environmental sustainability are key considerations. Programs like the Kimberley Process help eliminate conflict diamonds from entering the supply chain.
Choosing ethically sourced diamonds ensures that their journey from mine to market benefits communities and protects nature.
Why Understanding a Diamond’s Journey Matters
When searching for information about natural diamonds, customers often look for transparency. Keywords like “diamond mining,” “diamond cutting,” “certified diamonds,” “ethical diamonds,” and “diamond market” are not just SEO phrases—they reflect real consumer concerns. Educating buyers about the entire journey builds trust and connects them with the true value of their purchase.
Retailers, jewelers, and diamond suppliers who share this knowledge in blogs and product descriptions can enhance their search engine ranking while also appealing emotionally to customers.
FAQs
Q1: How are natural diamonds formed?
Natural diamonds form under high pressure and temperature deep within the Earth’s mantle over billions of years.
Q2: What are the 4Cs of diamonds?
The 4Cs stand for Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight, which determine a diamond’s quality and value.
Q3: Where are most diamonds processed?
Around 90% of the world’s polished diamonds are cut and processed in Surat, India.
Q4: What is an ethical diamond?
An ethical diamond is sourced responsibly, free from conflict, with respect for people and the environment.
Q5: Why is diamond certification important?
Certification from trusted labs like GIA ensures the diamond’s authenticity and gives buyers confidence in their purchase.